Skeletal System Overview - Bone Composition
Objectives
- Identify the cellular components of bone.
- Identify the acellular components of bone.
Click on each thumbnail to view detailed image
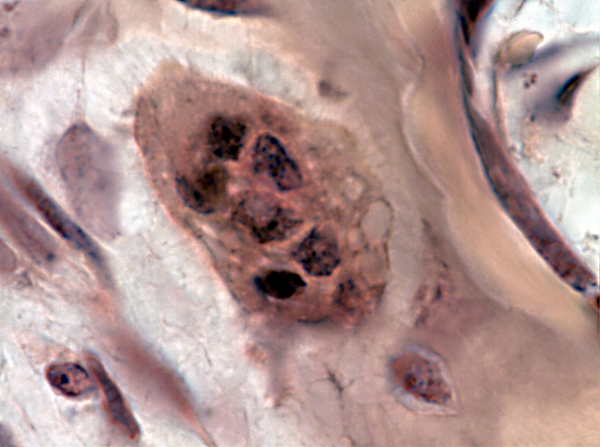
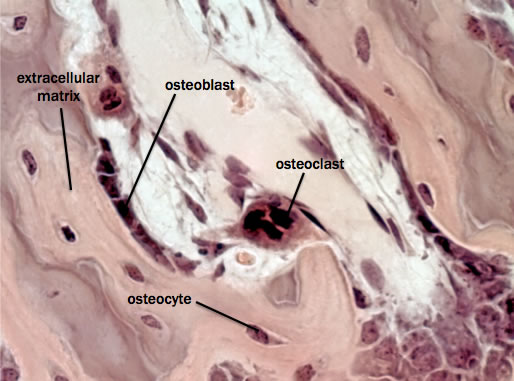
Bone consists of cellular and extracellular components.
Cellular components
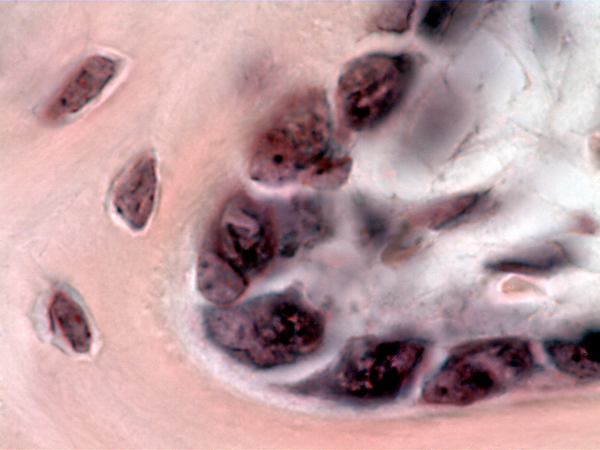
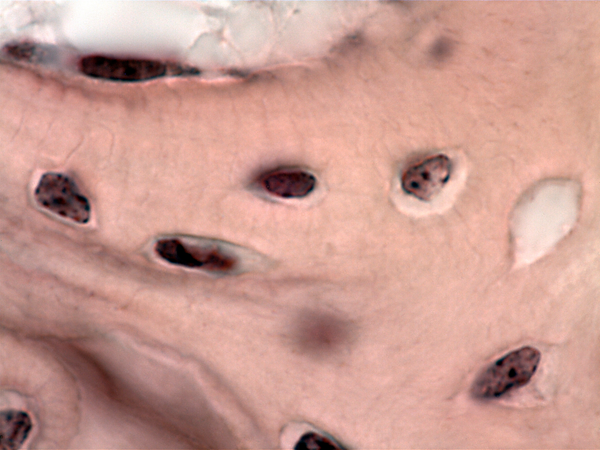
Stem cells known as osteoprogenitor or osteogenic cells give rise to immature bone cells called osteoblasts. The osteoblasts deposit bony matrix and once surrounded by that matrix, they are known as osteocytes.
Extracellular components
The bone cells are surrounded by extracellular matrix composed of collagen fibers and ground substance including calcium carbonate and calcium phosphate.