Integumentary System Overview
Objectives:
- Identify the functions of the integument.
- Identify the gross and microscopic anatomy of the skin including the epidermis and dermis.
- Understand the structure and function of the skin layers.
- Identify the structure and function of integument accessory structures: glands, hair, and nails.
Skin - Click on each label to view definition
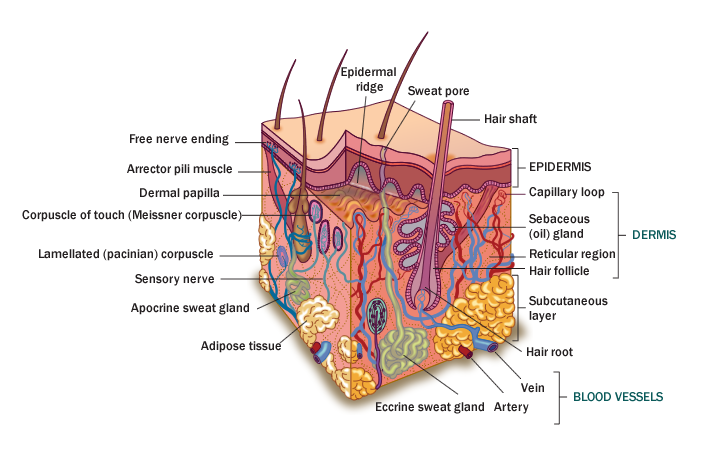
Introduction:
The integument is composed of the skin and associated structures including hair, nails, sensory receptors and glands. It forms a physical barrier between the external environment and the body. This barrier prevents blood and fluid loss and provides protection against physical trauma, bacteria, viruses, parasites, chemicals, and ultraviolet radiation.
Structure:
The skin is composed of two layers: the epidermis and dermis.
Function:
- Protection.
- initial steps of vitamin D formation.
- location for various sensory receptors for touch, pressure, vibration, hot, cold, and pain.
- excretion of water, metabolic wastes and electrolytes in perspiration.
- Body temperature regulation (Thermoregulation) via evaporation of perspiration on the skin surface and the movement of blood within the deep layer of the skin.