Hair
Objectives
- Identify the functions of nails.
- Identify the structure of nails.
Click on each label to view definition
Function
Nails function in scratching and helping with the grasping of small items. Nail health and appearance can provide clues about the health of a patient. Anemias, nutritional deficiencies and even respiratory disorders can manifest changes in the nails.
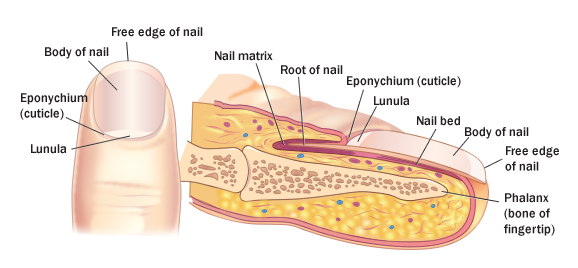
Structure
Nails are derived from the stratum corneum and contain keratin. Cells at the nail matrix undergo mitosis allowing for the continued lengthening of the nail plate.